Not an official ACM page
[1994 ACM finals problem set
| My ACM problem archive
| my home page]
1994 ACM Scholastic Programming Contest Finals
sponsored by Microsoft ®
Problem H
Monitoring Wheelchair Patients
 A researcher at a rehabilitation facility is studying the use that a
patient makes of a motorized wheelchair in a restricted area at the
facility. The chair's motor is connected to the axle by a chain
drive. Therefore both wheels turn at the same speed and the chair can
travel only in a straight line. The patient can stop the chair, rotate
the wheels, and thereby change the direction only while the wheelchair
is stopped. To help monitor its usage, the chair is equipped with a
compass, a clock, and a speedometer. A recording device records each
time interval that the chair is in motion, the average speed during
the time interval, and the compass bearing during the time
interval. The compass is a standard compass in which 0°
is north, 90° is east, and so forth.
A researcher at a rehabilitation facility is studying the use that a
patient makes of a motorized wheelchair in a restricted area at the
facility. The chair's motor is connected to the axle by a chain
drive. Therefore both wheels turn at the same speed and the chair can
travel only in a straight line. The patient can stop the chair, rotate
the wheels, and thereby change the direction only while the wheelchair
is stopped. To help monitor its usage, the chair is equipped with a
compass, a clock, and a speedometer. A recording device records each
time interval that the chair is in motion, the average speed during
the time interval, and the compass bearing during the time
interval. The compass is a standard compass in which 0°
is north, 90° is east, and so forth.
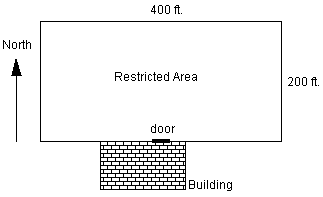
A map of the restricted area is shown. The restricted area is a 200 ft
by 400 ft rectangular area of the lawn. Patients enter the restricted
area from the door of a building located on the southern edge of the
restricted area. The door is at the center of the 400 ft southern
boundary, as shown in the figure.
The recording device turns itself on when the patient enters the
restricted area through the door and monitors the patient's movements
for up to 1 hour. Time is measured in seconds from 0 to 3600, with
time 0 being the time the patient initially enters the restricted area
through the door. The device records 4 numbers to describe the motion
of the wheelchair during any interval when the motor is in
operation. The first two numbers give the time the motion begins and
ends; the third number gives the speed during the time interval; and
the fourth number gives the compass bearing during the time
interval. (During each time interval the wheelchair maintains constant
speed and bearing.) For example, the recorded line
10.6 15.9 2.8 274
would indicate that between times t1 = 10.6 and
t2 = 15.9 seconds the wheelchair was traveling at speed of
2.8 ft/sec with compass bearing (direction) 274°. Times are
recorded to 0.1 sec, speeds are recorded to 0.1 ft/sec, and bearings
are recorded to a whole number of degrees.
Your job is to analyze the data from the wheelchair's recording
device. Specifically, you must determine the following:
- Did the patient ever leave the restricted area? If so, determine
the first time that the patient left the restricted area and determine
at what point on the perimeter of the restricted area the wheelchair
crossed out of the restricted area. If the patient did not leave the
restricted area, what was the distance from the door to the farthest
point the patient reached within the area?
- What was the total distance that the patient traveled?
For the purpose of answering these questions, use coordinates with the
location (0,0) corresponding to the southwest corner of the restricted
area and the location (400,200) corresponding to the northeast
corner. Since the recorder switches on when the patient passes through
the door, the position of the patient at time t = 0.0 is always
(200,0). Patients will be traveling north when they enter the
restricted area.
Input
The input data consists of several data sets. The first line of each
data set has an integer which is the number of lines recorded by the
device. Each subsequent line in the data set consists of the four
numbers recorded by the device during a particular time interval. The
end of data is indicated by a data set whose first line consists of
the number 0.
In the first data set of the sample input, the patient entered through
the door (at time 0.0) and for the first 5 seconds was traveling due
north at 3 ft/sec. From time t = 7 to t = 9 he traveled at a speed of
2 ft/sec with a compass bearing of 30°. He then stopped, changed his
bearing to 60°, and then traveled at 4 ft/sec from time t = 10 to time
t = 100. Ten seconds later (at time t = 110) he headed due north at 2
ft/sec until t = 200.
Output
The output for each data set begins with an identification of that
case. The output indicates whether the patient departed from the
restricted area and if so the time and point of departure on the
perimeter . If not, the maximum distance the patient reached from the
door is provided. For each case, the total distance that the patient
traveled is provided. Format your output so that the same labeling
information is included as shown in the sample output, with a line of
asterisks separating the cases.
Sample Input
4
0.0 5.0 3.0 0
7.0 9.0 2.0 30
10.0 100.0 4.0 60
110.0 200.0 2.0 0
3
0.0 20.0 2.0 0
500.0 600.0 1.0 270
3000.0 3100.0 1.0 0
7
0.0 5.3 2.1 0
19.8 35.6 2.7 346
42.0 78.4 2.3 15
1181.4 1192.1 1.7 117
2107.0 2193.6 2.1 295
2196.3 2201.2 2.0 298
2704.3 2709.2 1.5 208
0
Output for the Sample Input
Case Number 1
Left restricted area at point (400.0,132.8) and time 67.2 sec.
Total distance traveled was 559.0 feet
***************************************
Case Number 2
No departure from restricted area
Maximum distance patient traveled from door was 172.0 feet
Total distance traveled was 240.0 feet
***************************************
Case Number 3
Left restricted area at point (67.0,200.0) and time 2191.4 sec.
Total distance traveled was 354.7 feet
***************************************
Assumptions and requirements
- Within each data set, time intervals will be listed in
chronological order, with the first time interval always having time
0.0 as the time of entry into the restricted area. All times will be
given with one decimal place accuracy and will be in the range 0.0 to
3600.0 inclusive. For each time interval specified, the duration of
the time interval will be positive, i.e. the second time specified
will be greater than the first.
- Speeds will be in the range 0.1 to 9.9 ft/sec.
- Compass bearings will be given as a whole number of degrees and
will be in the range 0 to 359 inclusive. The initial compass bearing
for the first line of data in each data set will be 0.
- Within each line of data, numbers will be separated by at least
one blank space.
- All numerical results will be displayed with one decimal place of
accuracy as shown in the sample output.
- If the patient goes out of the restricted area, his location may
include negative coordinates. However, you don't have to worry about
the wheelchair crashing through the walls of the building.
This page maintained by
Ed Karrels.
Last updated September 20, 1999

